6. 📚 Home Task
The home task should be done using TypeScript.
Graph generator
As an implementation of this home task, you should create an application that allows creating a weighted graph and keep it as an adjacency list. For that, you need to implement WeightedGraph interface
interface WeightedGraph<T> {
addVertex(key: string): void;
addEdge(vertex1: T, vertex2: T, weight: number): void;
}
so that for a graph
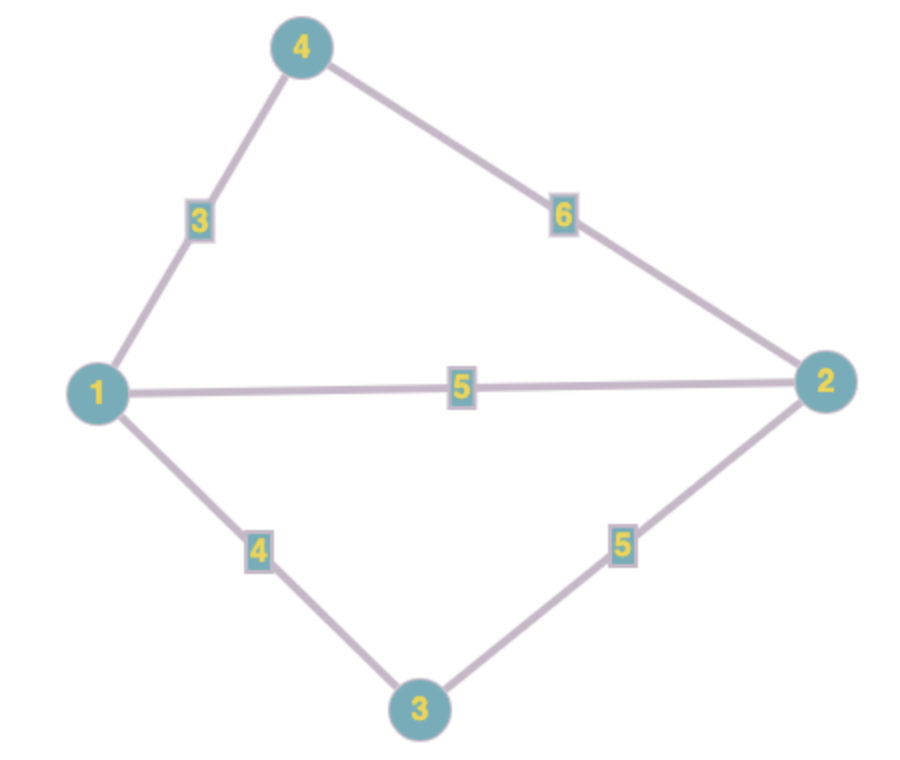
you can use your implementation of WeightedGraph interface to represent it in code
const vertices = [
new Vertex('1'),
new Vertex('2'),
new Vertex('3'),
new Vertex('4'),
new Vertex('5')
];
const edges = [
new Edge(vertex1, vertex4, 3),
new Edge(vertex1, vertex2, 5),
new Edge(vertex1, vertex3, 4),
new Edge(vertex2, vertex4, 6),
new Edge(vertex2, vertex3, 5),
];
const graph: WeightedGraph = new <Your WeightedGraph implementation>;
vertices.forEach(verticle => graph.addVertex(verticle));
edges.forEach(edge => graph.addEdge(edge.from, edge.to, edge.weight));
Find the shortest path
The application should have the possibility to find the shortest paths from one vertex to others (findAllShortestPaths method) and to find the shortest path between two vertexes (findShortestPath method). For that, you should implement the Dijkstra interface bellow
interface Path {
path: string[];
distance: number;
}
interface Dijkstra<T> {
findShortestPath(vertex1: T, vertex2: T): Path;
findAllShortestPaths(vertex: T): Record<string, Path>;
}
and use it like bellow
const dijkstra: Dijkstra = new <Your Dijkstra implementation>(graph);
dijkstra.findShortestPath(vertex4, vertex3); // { path: ['4', '1', '3'], distance: 7 }
dijkstra.findShortestPath(vertex1, vertex5); // { path: [], distance: Infinity }
dijkstra.findShortestPath(vertex1, vertex1); // { path: ['1'], distance: 0 }
dijkstra.findAllShortestPaths(vertex4);
/*
{
'1': { path: ['4', '1'], distance: 3 },
'2': { path: ['4', '2'], distance: 6 },
'3': { path: ['4', '1', '3'], distance: 7 },
'5': { path: [], distance: Infinity }
}
*/
Your application should work with much more complex graphs. The one provided above is just an example.
Evaluation criteria
- Only graph generator is implemented.
- Graph generator is implemented and only one of the methods of
Dijkstrainterface is implemented correctly. - Graph generator is implemented and both methods of
Dijkstrainterface are implemented correctly with minor issues with regard to edge cases. - Graph generator is implemented and both methods of
Dijkstrainterface are implemented correctly without any issue.